Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that allows secure mutual authentication. This service can be leveraged by non-web based applications, workstations, and servers for fast, secure authentication. Kerberos currently handles the authentication for a number of services, including CAS and LDAP.
The University’s implementation of Kerberos utilizes the OpenLDAP cluster as its database rather than the standard flat file. This configuration allows for better data consistency and redundancy. The current infrastructure has administrative servers and KDC (Key Distribution Centers) separated out into different areas of the infrastructure to facilitate proper data replication among all of the nodes.
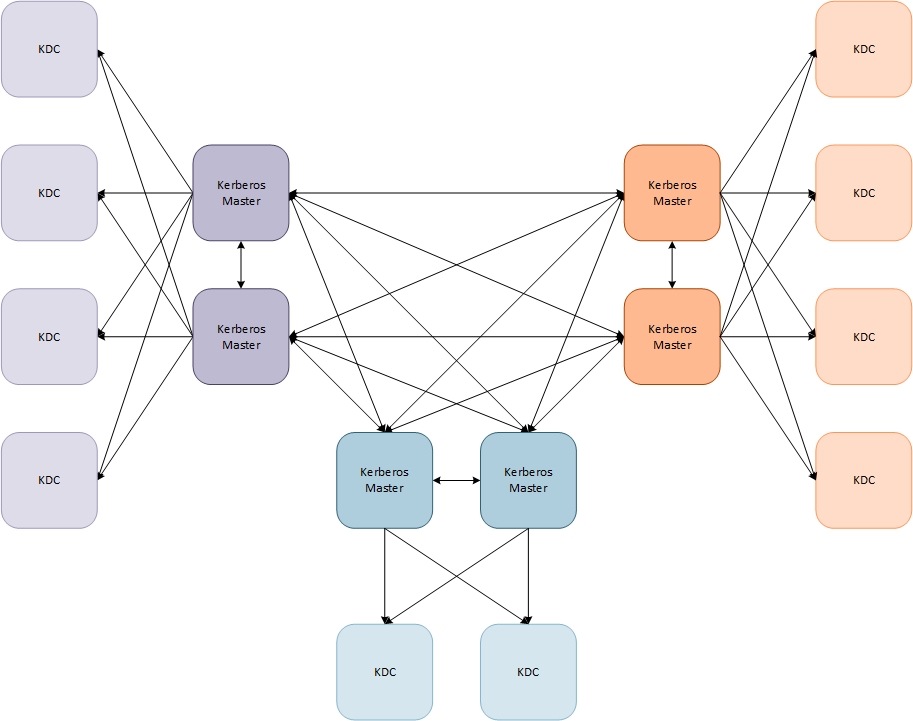
The diagram above shows the Kerberos specific functions of the servers, overlaid on the OpenLDAP infrastructure. The nodes shown above are distributed between our two data centers and Azure. Under nominal conditions all Kerberos & KAdmin requests will be pointing at one of the replica or master nodes respectively. We have a high-availability pair of load-balancers that will forward requests to the least busy non-Azure node. The name spaces (i.e. kerberos.uconn.edu and kadmin.uconn.edu) are controlled by our Infoblox system. In cases of a disaster, one of the Infoblox nodes, either on campus or in Hartford will automatically re-point the workload to Azure.